As part of the Level 4 Software Developer Apprenticeship, I have to complete a Knowledge Module exam. The exam is called BCS Level 4 Diploma in Software Development Methodologies. You can find the syllabus here.
[The module] covers the range of concepts, approaches and techniques that are applicable to Software Development Methodologies, for which Apprentices are required to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding.
BCS
As part of this module, there are three main sections:
- The Software Development Life Cycle
- Software Development Methodologies
- Data Roles and Responsibilities
After watching a video provided by Makers Academy, and also attempting the specimen paper provided by BCS, I have written some notes. I wanted to share those notes for anyone else who is going to attempt this exam!
Update
I passed my exam! I was able to finish in 10 minutes and got 88% correct! 🎉
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
The SDLC provides a set of steps that can be used to develop software.
There are seven stages to the SDLC:
- Feasibility Study
- Requirements Analysis
- Design
- Code Development
- Testing
- Deployment/Implementation
- Maintenance
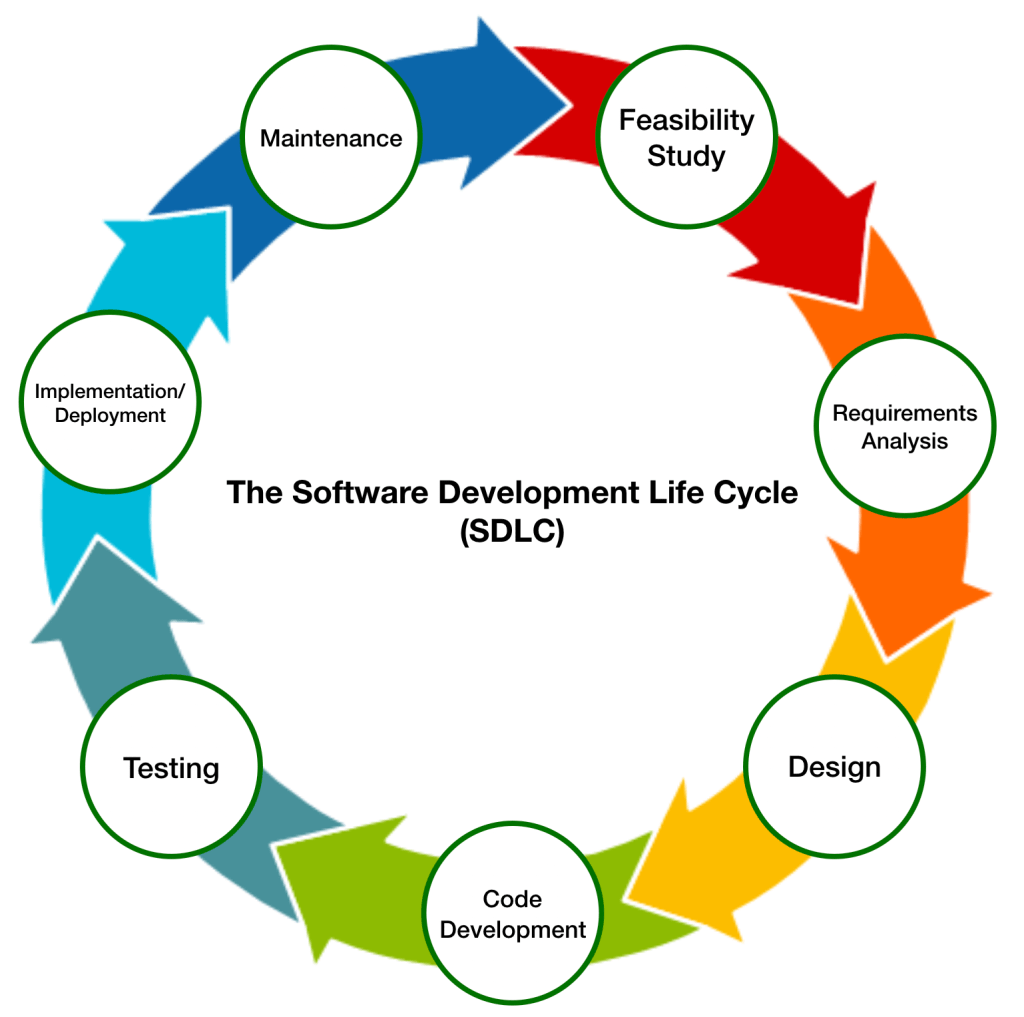
Each stage should have a deliverable, which is passed from one stage of the SDLC to the next.
The purpose of a deliverable is to enable the next stage to happen.
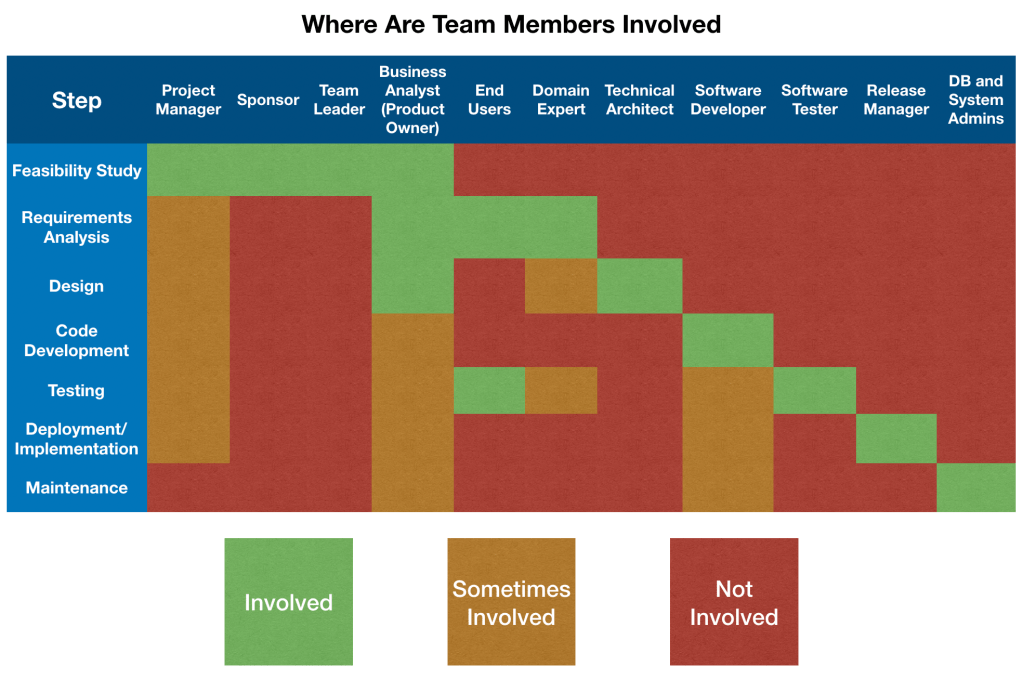
The stages also have people who own and deliver these stages, this can be seen in the below diagram.
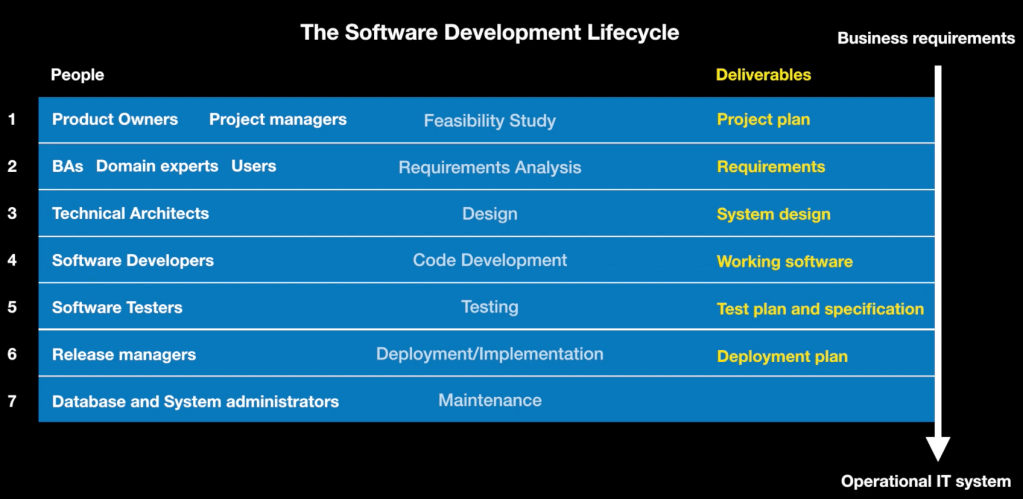
People can move accross different stages however, to utilise their skills in more than one place.
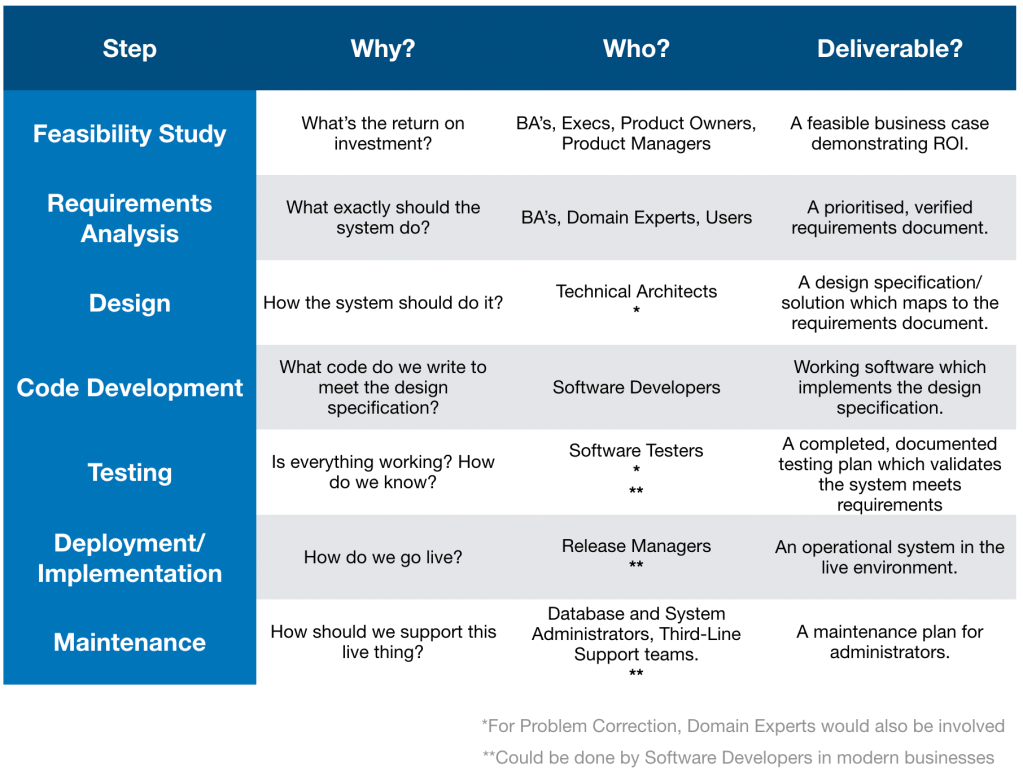
Feasibility Study
The Feasibility Study tries to find out what is the return on investment from completing the project.
Product Owners and Managers try to convince the business that a project is worthwhile and create a project plan.
Business Analysts get involved with Feasibility Study too, to find out if the idea will return a good return on investment
The deliverable from this would be a feasible business case demonstrating ROI.
Requirements Analysis
Here we are trying to pinpoint what the system actually needs to do.
Business Analysts work with Domain Experts and Users to nail down the exact requirements for the product.
A Domain Expert is a person with special knowledge or skills in a particular area of endeavour. They have a deep understanding of and can provide insight into the business’ products or programs.
Traceability and cross-referencing is used to determine requirements.
There are two ways to capture requirements:
- Functional Requirements – the system must do this
- Non-Functional Requirements – the system must be like this
- for example: being user friendly, reliable, secure, accessible, available, etc…
User Stories are also generated as part of this stage.
Out of this stage a prioritised and validated requirements document should be generated.
Design
Here we figure out how the system should achieve the requirements.
Technical Architects try to produce a system design to meet the given requirements.
Business Analysts tend to be involved here too.
There are four high level areas:
- Input/Output designs (e.g user interfaces)
- Data designs (e.g database structure)
- Security and Control designs (avoid being hacked)
- Process designs (flow of information)
- Universal Modeling Language (UML)
- Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERD)
- State Transition Diagrams
- Sequence Diagrams
- Interaction Diagrams
The deliverable from this stage is a solution to the requirements document, in the form of a design solution (or design specification).
Code Development
Code needs to be written to meet the design specification.
The system, or at least part of the system, has been designed, so development can begin.
Software Developers build to the design specification.
Out of this stage we should get working software which implements the design solution.
Testing
We need to test that everything is working, and working as it should be.
Software Testers create a thorough test plan and test scripts to ensure everything meets the design and the requirements.
Software Developers often get involved with testing.
Business Analysts also get involved, as they can bring Users with them to try the product out.
A completed, documented test plan validating the system meets all requirements should be generated from this step.
Deployment/Implementation
If all went well with Testing, we can deploy our application live.
Release Managers produce a deployment plan to get the product live.
Software Developers are usually heavily involved.
In modern companies, Release Managers may not exist, as there may be a CI/CD pipeline managed by the Software Developers or Testers.
From this stage we should have an operational system in the live environment.
Maintenance
Supporting our system.
Covers all the supervision a live product needs including.
- Bug Fixes
- Enhancements
- Administration
From this, maintenance plans should be produced for administrators and support teams.
TL;DR (Too Long Didn’t Read)
If you don’t want to read all of that, here is the short version:
The SDLC provides a set of steps that can be used to develop software.
Software Development Methodologies
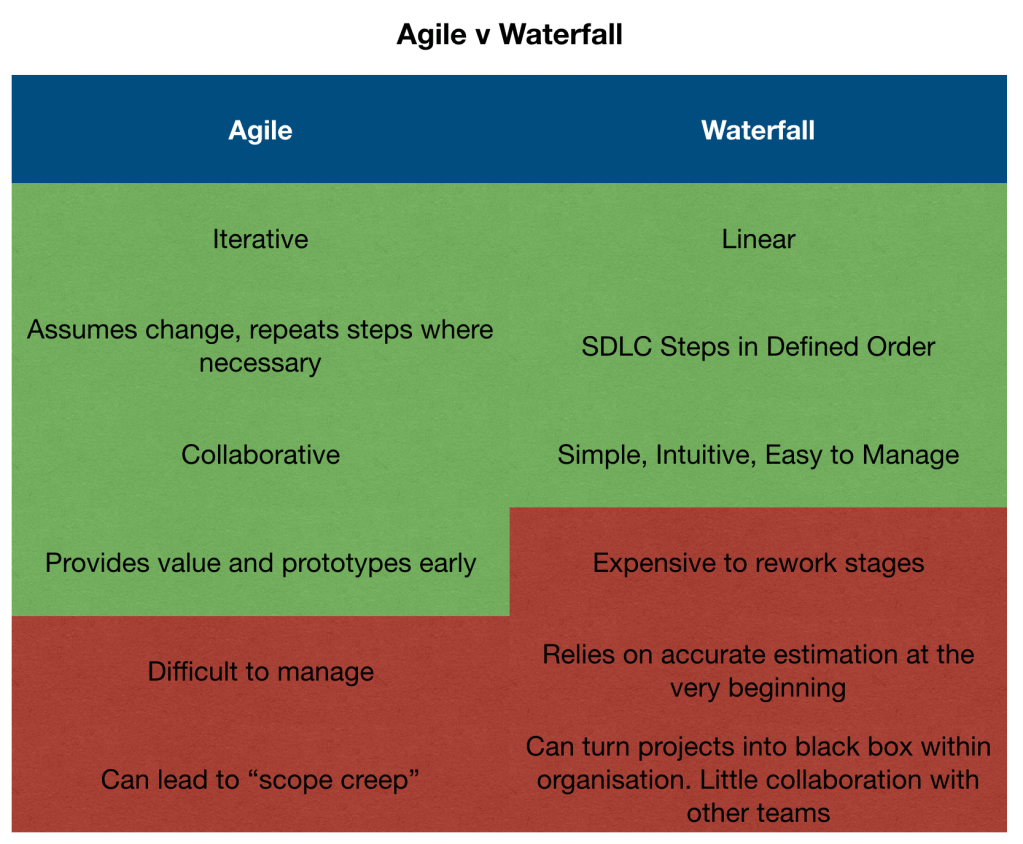
There are lots of different methods for software development, but the main two specified in the syllabus are Waterfall and Agile.
The main differences between them are the order you do the stages of the SDLC and how often you repeat them.
Waterfall
In Waterfall, you do the stages in order, only start one step once the previous step is done. This means it is linear (or sequential). You do not go back to a previous stage unless you are prepared to re-start the work in the stage you are currently in.
Each stages deliverables are signed off to ensure you are ready to move on.
The problem with this is if any of the business requirements change, then the first 3 steps have to be re-done.
Agile
Still uses the SDLC, but quicker.
Short, iterative, repeated loops of the cycle, with lightweight deliverables.
Agile also encourages the people who specialise in each stage to work across multiple stages, and allows you to move back and forward across the stages when new information becomes available.
Speed of work and frequent iterations of software being delivered allows for greater communication between teams and users.
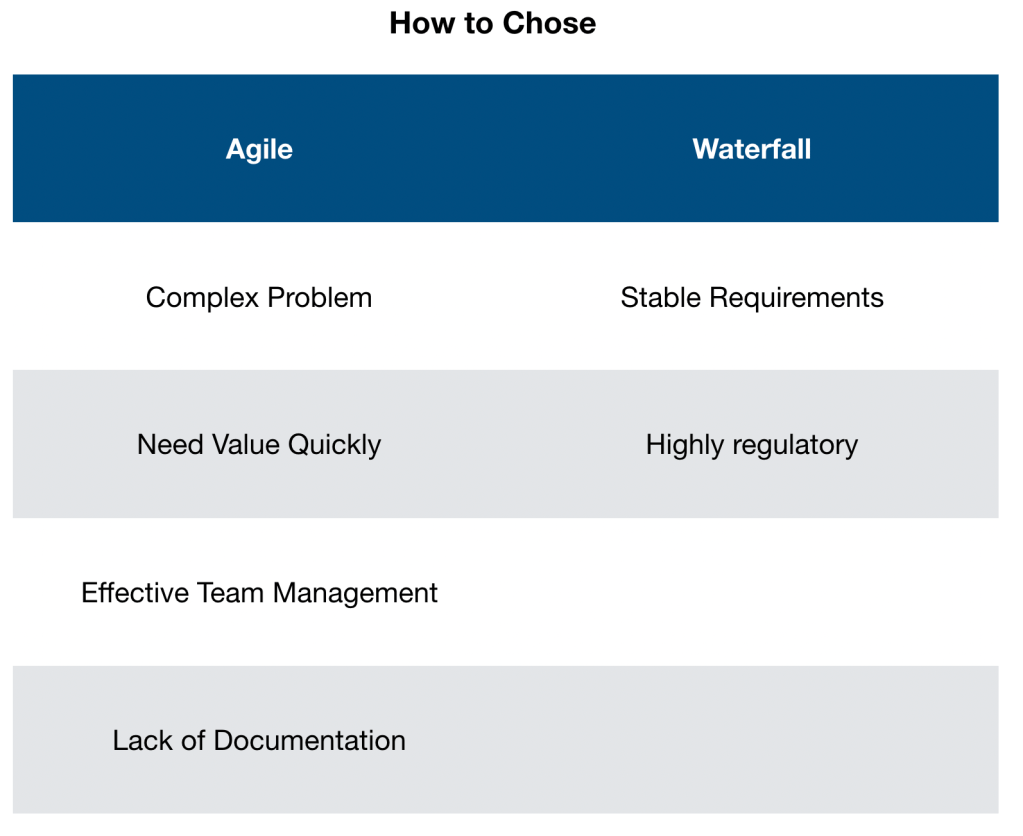
Choosing Between the Two
When trying to decide between the two you must consider a few things.
If things are likely to change, then Agile is better. If you are working on something you have done lots of times before, and the requirements are set, then Waterfall is easier to manage
Agile‘s prototype first approach delivers value rapidly, where Waterfall takes longer to produce results. Agile also allows you to prioritise building high risk parts of the project first, allowing you to discover potential problems earlier on before cost has been incurred.
Where Agile delivers working value continuously, Waterfall projects that fail deliver nothing at all.
If you are building a product in a heavily regulated space, Waterfall may be the better approach as its less experimental. You can specify all the requirements in detail up front, and formally review each deliverable before any work in the next stage can get started.
If you want more collaboration between teams, Agile would be the way to go.
TL;DR
Other Software Development Methodologies
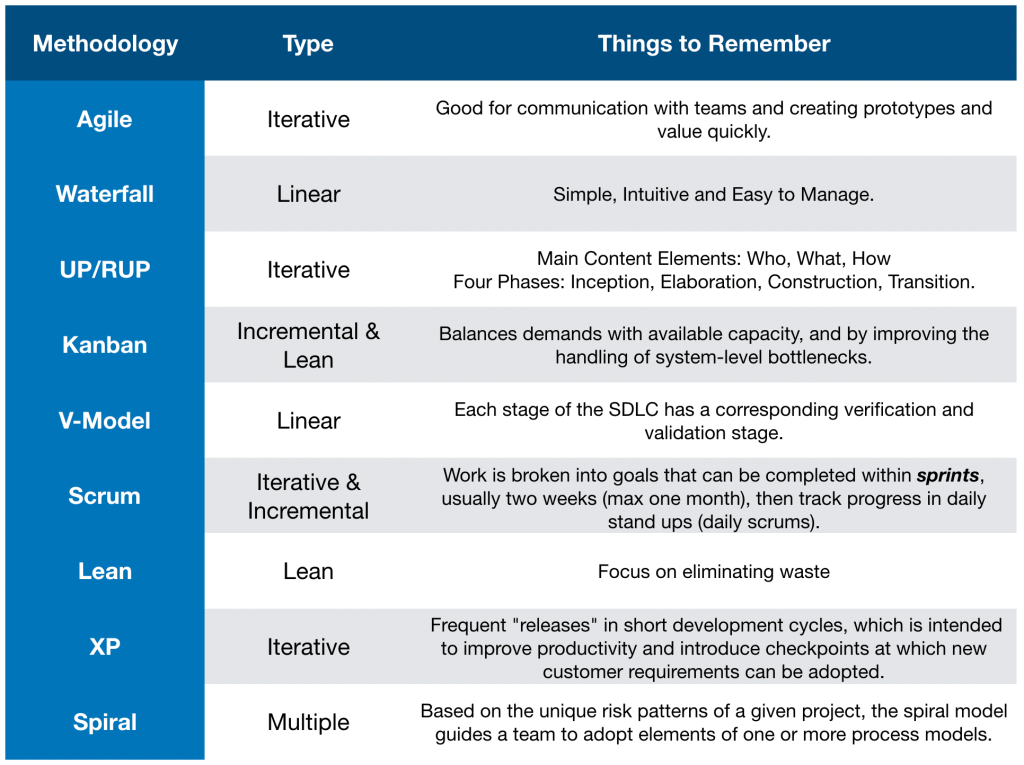
There are many other methodologies outside of Agile and Waterfall which are not mentioned in the syllabus but have come up in the mock paper, so here are some examples you should know about.
Unified Process (UP)/ Rational Unified Process (RUP)
(Rational) Unified Process is an iterative and incremental software development process framework.
As a generalisation, UP is better suited for larger teams on larger projects where you won’t always have face to face communications. Agile works better on smaller teams and smaller projects. UP is generally more document heavy than Agile too.
Kanban
Based on the Agile framework. Kanban is a lean method to manage and improve work across human systems.
V-Model
V-Model represents a development process that may be considered an extension of the waterfall model.
Because it is Waterfall, Validation and Verification happen at every stage.

Scrum
Scrum is an agile process framework for managing complex knowledge work, with an initial emphasis on software development. It is designed for teams of ten or fewer members, who break their work into goals that can be completed within timeboxed iterations, called sprints, no longer than one month and most commonly two weeks, then track progress and re-plan in 15-minute time-boxed daily meetings, called daily scrums.
Spiral
The spiral model is a risk-driven software development process model. Based on the unique risk patterns of a given project, the spiral model guides a team to adopt elements of one or more process models.
Lean
Based on the Agile framework. Lean development can be summarised by seven principles, very close in concept to lean manufacturing principles:
- Eliminate waste
- Amplify learning
- Decide as late as possible
- Deliver as fast as possible
- Empower the team
- Build integrity in
- Optimise the whole
XP
Extreme programming (XP) is a software development methodology which is intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. As a type of agile software development, it advocates frequent “releases” in short development cycles, which is intended to improve productivity and introduce checkpoints at which new customer requirements can be adopted.
TL;DR
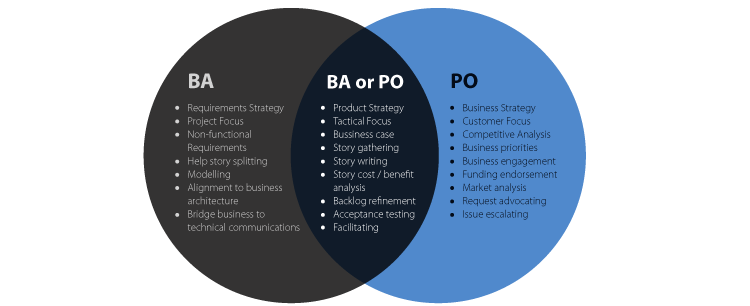
Data Roles and Responsibilities
Who works in a software project team:
Business Roles
- Sponsor
- Business Analyst (Product Owner)
- Domain Expert
- Users
Project Roles
- Project Manager
- Team Leader
Technical Roles
- Technical Architect
- Software Developer
- Software Tester
Implementation/Support Roles
- Release Manager
- DB Administrator
- System Administrator
Above I have put Business Analyst and Product Owner together, as their roles are very similar and have many overlapping responsibilities. Businesses can generally have a hybrid role combining the two, but both roles may exist in a team.
TL;DR


Sample Paper
I wanted to go through the sample paper and explain the answers, so if you plan on using the mock don’t read this part! The answers to the specimen paper can be found here. I will add the explanations from the answer key in italics.
Question 1
Which stage of the software development lifecycle (SDLC) would include the following activities:
- Consideration of the potential risks involved in developing software.
- Determining whether the project outcome will be worth the costs involved.
A Implementation / Deployment.
B Requirements Analysis.
C Testing.
D Feasibility Study.
Answer
D Feasibility Study
These activities take place as part of the feasibility study itself and business case development, which takes place during the feasibility study stage of the SDLC.
Considering risk and whether the project outcome is worth the costs is how you can figure out your Return On Investment, which is a key part of the deliverable from the Feasibility Study, hence the answer is D.
It would not be Requirements Analysis, as this is focussed on what the system should do, not whether or not it should be done.
It would not be Testing or Implementation/Deployment as they happen after the Development stage, which is too late to just start thinking about risks and the ROI!
Question 2
Which of the following is a purpose of the software development lifecycle (SDLC)?
A To provide a suitable framework for planning a software development project.
B To provide a set of steps to create a software end-product.
C To create a methodology for developing software code.
D To provide a consistent set of coding standards.
Answer
B To provide a set of steps to create a software end-product.
As defined in the syllabus the SDLC provides a set of steps that can be used to develop software.
I found this one a bit tough at first as it seems like all the answers are saying the same thing, but reading into it a bit more carefully it became clearer.
It can’t be C as it talks about methodology for specifically developing software code. Whilst this is a step in the SDLC, it is not the only aim of it.
Similarly it cannot be D as the SDLC doesn’t give you any details on how to actually code the project, you can use whatever standards fit the project.
A looks more feasible as it talks about the whole project, but it only mentions the planning aspect. The SDLC covers all stages of a project, from the planning right through to delivery and maintenence.
Therefore it must be B, the SDLC does give you steps to create a software end-product from beggining to end.
Question 3
Which sequence puts the following stages in the SDLC in the CORRECT chronological order?
a) Testing.
b) Requirements Analysis.
c) Maintenance.
d) Design
A b, d, a, c.
B b, d, c, a.
C d, b, a, c.
D d, b, c, a.
Answer
A b, d, a, c.
Demonstrates understanding of how the SDLC is implemented as required by section 1.2 of the syllabus.
Not much to say about this one, more of a test of memory.
If you wanted to try and figure it out logically you could look at each step and see if it makes sense without one of the others. For example, you cannot do Maintenance until the software is deployed, which means it must have been Tested. If its been tested it must have been developed at some point, based on a Design. The design needs to be based on a set of requirements, which come from the Requirements Analysis.
Question 4
Which of the following is NOT an iterative methodology?
A Waterfall.
B UP / RUP.
C Scrum.
D Spiral.
Answer
A Waterfall.
The waterfall method is sequential not iterative. Iterative development contrasts with a traditional waterfall method in which each stage of the software development life cycle is “gated.” For waterfall development coding doesn’t begin until design of the entire software application is complete and has gone through a stage gate review. Likewise, testing doesn’t begin until coding is complete and has passed necessary phase gate reviews.
Again more about if you remember the different methodologies. The BCS syllabus only mentions Waterfall and Agile, so when I saw this question I had no idea what the others were. I thought it was a bit unfair to ask questions on things not in the syllabus. However, technically you do only need to know about those two, as if you know what Waterfall is, you know the answer is A, as Waterfall is not iterative.
Question 5
Which software development method allows software to be deployed for client use after each iteration?
A Agile.
B UP.
C V-Model.
D Waterfall.
Answer
A Agile.
With the agile method, each feature is taken from start to finish within an iteration, with the software being released for deployment at the end of each iteration, or if appropriate even during an iteration.
Another question with methodologies not mentioned in the syllabus. That said, we can immediately ignore D as we know Waterfall is not iterative. Agile we know is good for quick development of prototypes and collaboration with the client, so it is safe to assume the answer is A from the knowledge given to us by the syllabus.
If you do more research, you know that it isn’t C as V-Model is a type of Waterfall, it is not iterative.
UP is iterative as well, so you could be tempted to go for B. However with up, the development is iterative, but it only goes as far as testing. The deployment phase does not happen iteratively, instead being released in chunks at certain time frames.
Question 6
Which of the following is a role of a domain expert?
A To provide insight into business products and processes.
B To specify functional requirements on behalf of the customer.
C To identify non-functional requirements.
D To assess project risks and constraints.
Answer
A To provide insight into business products and processes.
A domain expert is a person with special knowledge or skills in a particular area of endeavour. They have a deep understanding of the business’ products or programs.
The answer is A as Domain Experts should have vast knowledge of the business and its processes, so they are best placed to provide insight.
It would not be B as the Users should be providing requirements for themselves. C is again about requirements, which may not be best for a Domain Expert to provide as they are generally experts in a specific area, and may not be able to cover all aspects. D should really be done as part of the Feasibility Study which happens before the Domain Expert gets involved.
Realistically, in an actual business, Domain Experts are probably involved in many of these areas, but their actual defined role as per the syllabus is above, that’s what you need to remember.
Question 7
A software application used by the general public has been found to have a security weakness. The problem has been diagnosed and a development project initiated to correct the security weakness. The project team will include security domain experts.
At which stages in the development will it be the MOST important to involve the domain experts?
A Feasibility study, code development.
B Design, testing.
C Requirements analysis, maintenance.
D Initiation, implementation / deployment.
Answer
B Design, testing.
Because this is problem correction, the requirements are clear. Design will be crucial to ensure the security weakness is designed out, and testing to ensure that appropriate tests of security are carried out.
As far as I remember this was not covered in the syllabus or the Makers video, so it was a bit tougher. The answer is B for the reason above. Because this is a fix for a problem, the requirements are clear, fix the problem! A security domain expert isn’t needed for this, but they will be very useful in the how? part. So it is important they are involved in Design. Simularly it is important they are involved in Testing as a security domain expert knows what to look for. The key for this question was realising that they are specifically a security domain expert.
It would not be A as there isn’t really a Feasibility Study needed, there is a problem that needs fixing. It isn’t C as there is no Requirements Analysis, again the requirements are clear, the product needs to be secure. Finally it isn’t D as implentation/deployment should be business as usual, no need for a security domain expert to help. Initiation again was not covered in the syllabus, so I didn’t know what this was at first, but it is a step before the Feasibility Study where the business need is identified. It exists in the 10 step version of the SDLC, but the syllabus only talks about the 7 step version. The 10 step version looks like this:
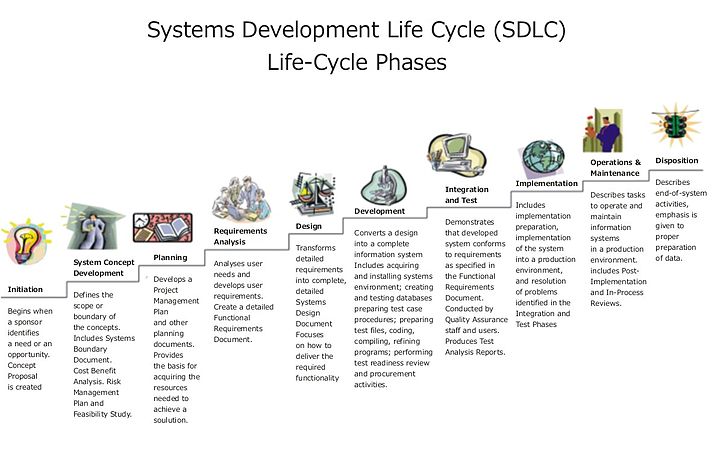
Question 8
During the design stage of the SDLC, which of the following would be developed?
A Software specification.
B Software code.
C Use cases.
D Test plans.
Answer
A Software specification.
The design phase considers and develops a blueprint for the software solution that will be implemented in live operation. The design may need to go through several iterations to ensure the system specification describes a final product that will successfully meet your business needs.
The answer is A, as the Design stage should produce a design specification as a deliverable. This is then used to develop the software.
It would not be B as developing software code is part of the Software Development step which comes after Design.
It would not be C as use cases are created in the Requirements Analysis stage prior to Design.
It is also not D as test plans are created in the Test step once the code is written.
Question 9
Which of the following is a purpose of applying traceability and cross-referencing between software development deliverables?
A To identify requirements which have not been met.
B To determine which deliverables might be affected by a change request.
C To assist in tracking project management issues
D To ensure that deliverables are delivered in priority sequence.
Answer
A To identify requirements which have not been met.
Traceability and cross-referencing is used to determine requirements.
The syllabus provides no information on traceability and cross-referencing so this was a tough question.
Traceability in software engineering is the ability to trace work items across the development lifecycle. It’s used to keep track of what’s going on in the development lifecycle — and show what’s happened.
https://www.perforce.com/blog/alm/what-traceability
Traceability works by linking two or more work items in application development. This link indicates a dependency between the items. Requirements and test cases are often traced.
Specifically requirements traceability
Requirements are traced forward through other development artifacts, including test cases, test runs, and issues. Requirements are traced backward to the source of the requirement, such as a stakeholder or a regulatory compliance mandate.
https://www.perforce.com/blog/alm/what-traceability
The purpose of requirements traceability is to verify that requirements are met.
So you just have to know that the answer is A!
If my understanding is correct, you can rule out B, C and D because traceability is about tracking the progress of a requirement or deliverable, not necessarily tracking it against other requirements and deliverables. As they are in isolation, you wouldn’t be able to see how they are effected by other changes as mentioned in B and C. Also you can’t see them vs eachother, so it can’t be D.
Question 10
Interaction diagrams are a deliverable of which stage of the SDLC?
A Design.
B Analysis.
C Code Development.
D Implementation (Deployment).
Answer
A Design.
The design phase is where you will look at many potential solutions and determine the most effective way to construct the solution and the structure of components you will build.
The answer is A, as the Design phase is where you produce all the diagrams. An interaction diagram lays out how the parts of the system will interact with eachother. You need to know this in order to write the code, so it cannot be C and therefore can’t be D either. It would not be B, as you do not need to know how things are going to work at the analysis stage, it is more about what the software needs to do.
Question 11
Which of the following factors would be a potential candidate reason for choosing an Agile method for a software development project?
A The development project consists of a large distributed team.
B The customer has very few formally documented requirements.
C There are strict safety critical requirements.
D The customer has a range of complicated contractual commitments that are linked to the planned development.
Answer
B The customer has very few formally documented requirements.
Agile does not need formally documented requirements, but requirements are worked through with the customer through the iterations of the development. The other options relate more to sequential / waterfall method.
The explanation in the answer key here is pretty good at explaining why it is B, but I will try to elaborate further.
It is not A as Agile is better when you have a smaller team. The strucure of Waterfall is better when working with a larger distributed team.
It is not C as again, Waterfall is better when dealing with critical and highly regulated requirements as it is less expiremental. Also all the requirements have to be specified in detial up front and each stage is signed off before continuing with the next, which leaves less room for error.
It is not D for similar reasons.
B is the answer as Agile is the best for if you have less known requirements. With Agile you can work with the requirements you do have and then review with the client what else is needed after each iteration.
Question 12
Which of the following would be responsibilities of the product owner in a software development project using an agile method of scrum?
a) Prioritising items on the backlog.
b) Accepting stories as done.
c) Managing the execution stage of the project.
d) Representing the customer to the Agile team
A b, c and d only.
B a, b and d only.
C a, b and c only.
D a, c and d only.
Answer
B a, b and d only.
The product owner has the responsibility of prioritising and managing the backlog especially in smaller teams / businesses. Therefore, B is the correct answer. Managing any part of the project is not correct, as the project manager would take on this role.
Again, thanks to the syllabus we know nothing about Scrum, however we are told it is Agile, so that does give us some information. The syllabus also gives us very little information on Product Owners, but they are similar to Business Analysts.
For me with this question, looking at the options, I know that product owners should not be involved with execution, therefore c) can’t be in the answer. That only leaves B as the right answer.
Aside from that, I know that product owners look after the stories, so it is their job to prioritise stories and mark them as done once the acceptance criteria has been met. This meant that the answer had to contain a) and b). As the product managers look after the user stories, they can represent the customer to the team, hence d) being correct as well.
Here is the definition of a Product Owner:
Product owner is a scrum development role for a person who represents the business or user community and is responsible for working with the user group to determine what features will be in the product release.
Scrum product owner responsibilities include:
https://searchsoftwarequality.techtarget.com/definition/product-owner
– Defining the features of the application.
– Prioritizing features of the application.
– Adjusting the features and priority as needed after each sprint or iteration.
– Accepting or rejecting work results.
– Accepting or rejecting work results.
And here is the definition of a Business Analyst:
BAs engage with business leaders and users to understand how data-driven changes to process, products, services, software and hardware can improve efficiencies and add value. They must articulate those ideas but also balance them against what’s technologically feasible and financially and functionally reasonable.
BA’s responsibilities include:
https://www.cio.com/article/2436638/project-management-what-do-business-analysts-actually-do-for-software-implementation-projects.html
– Creating a detailed business analysis, outlining problems, opportunities and solutions for a business.
– Budgeting and forecasting.
– Planning and monitoring.
– Variance analysis.
– Pricing.
– Reporting.
– Defining business requirements and reporting them back to stakeholders.
Question 13
A company is developing application software for use by the general public using the Scrum Methodology. Which of the following will NOT be a responsibility of the Scrum Master?
A Help the development team to achieve their goals.
B Remove impediments from the team.
C Shield the team from interruptions during the sprint.
D Lead the development team.
Answer
D Lead the development team.
The Scrum Master is there to help the team perform at their highest level, removing impediments and shielding the team from interruptions. The Scrum Master does not take on the role of a Lead Developer. They may have a technical role but being the Lead developer is not the responsibility of the Scrum Master.
The answer is D, as the Scrum Master is there to lead the team as whole. They represent the team to anyone outside of the team and do their best to ensure the team has everything they need to work. They are not involved with the actual development in detail.
The scrum master is the team role responsible for ensuring the team lives agile values and principles and follows the processes and practices that the team agreed they would use.
The responsibilities of this role include:
https://www.agilealliance.org/glossary/scrum-master/
– Clearing obstacles
– Establishing an environment where the team can be effective
– Addressing team dynamics
– Ensuring a good relationship between the team and product owner as well as others outside the team
– Protecting the team from outside interruptions and distractions.
Question 14
Which of the following are objectives of the maintenance stage of the SDLC?
a) Identify and fix bugs before software is implemented (deployed) so that they do not cause operational failures.
b) Adapt and modify the software as users’ needs change through time after implementation (deployment).
c) Complete any testing that could not be finished before implementation (deployment).
d) Fix bugs identified during live operation of the software.
A a and b only.
B a and d only.
C b and c only.
D b and d only.
Answer
D b and d only.
Software maintenance in software engineering is the modification of a software product after deployment to correct faults, to improve performance or other attributes, and make changes and modifications as required.
As we know Maintenence is the final stage of the SDLC. Therefore it cannot be a), as this is stating that it should fix bugs before the implementation/ deployment stage, which is incorrect. It also cannot be c) as there should not be any testing that has not been finished at this stage. The Implementation/ Deployment phase should only be started once Testing has finished and produced it’s deliverable.
d) is pretty much the main part of the Maintenence phase so will be included in the answer. b) is also correct as it occurs after implementation.
Question 15
Which of the following is a TRUE statement about the software development lifecycle (SDLC)?
A The SDLC should be used only with sequential development methodologies.
B The SDLC contains detailed instructions that should be followed to develop any IT system.
C The SDLC can be used to solve any business problem.
D The SDLC is independent of the software development methodology used.
Answer
D The SDLC is independent of the software development methodology used.
A software development lifecycle is essentially a series of steps, or stages that provide a model for the development and lifecycle management of an application or piece of software, that is not dependent on the development methodology used.
D is the right answer as we know the SDLC provides a set of steps that can be used to develop software. This means it doesn’t matter what method you use, these steps are going to be followed in some way.
A is incorrect as we can use the SDLC with any development methodology, sequential or otherwise. Agile is one of the most popular, and it is iterative not sequential.
B is incorrect as the SDLC does not provide steps on how to develop an IT system, it provides steps. The detail is worked on as part of the steps.
C is incorrect as the SDLC is only applicable to software projects, it will not solve every business issue.
Question 16
Which statement describes the use of the V-Model software development method in the software development lifecycle (SDLC)?
A All seven stages of SDLC are performed for each iteration, with verification and validation performed in the final stage.
B Each of the seven stages are performed iteratively before moving onto the next stage with verification and validation performed in the testing stage.
C The first three stages are performed once then verified and validated. The following four stages are iterative.
D Each stage of the SDLC has a corresponding verification and validation stage.
Answer
D Each stage of the SDLC has a corresponding verification and validation stage.
The V-model is SDLC model where execution of processes happens in a sequential manner in V-shape. It is also known as Verification and Validation model.
Once again there is a whole question about something that isn’t mentioned in the syllabus! The most important thing to know is that V-Model is linear (or sequential), and very similar to Waterfall. For this reason we can work out that the answer is D. This is because we know that in linear methodologies, each step has to be completed and have a deliverable before the next one can start. Therefore it cannot be A, B or C as each of them has the validation and verification happening only after certain steps, which is incorrect.
Question 17
A software development project is being initiated, and the project manager has set the following broad objectives for the software development team:
- Focus on the customers.
- Energise the team.
- Eliminate waste.
- Learn quickly.
- Keep improving.
Which of the following methodologies has a focus on eliminating waste?
A Unified Process (UP).
B Lean.
C Scrum.
D XP.
Answer
B Lean.
Lean programming is a concept that emphasises optimising efficiency and minimising waste.
Pretty much the whole point of Lean is to eliminate waste, so the answer is B. Not much more to say on this one, you just have to know it.
Question 18
A user guidance document has been developed alongside the development of software, to assist the users in operating and using the software. The introduction includes a ‘Change history’ table, and it contains the following details:
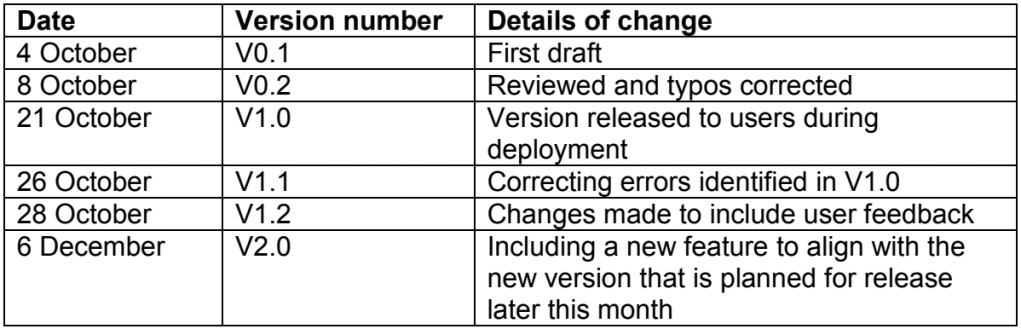
Which of the following are provided by this change history table?
a) An audit trail of the reasons for change.
b) Traceability of the source of changes.
c) Keeping track of the details of the change.
d) Providing information for stakeholders.
A a and c only.
B a and d only.
C b and d only.
D b and c only.
Answer
B a and d only.
Although the details are sparse, they include reasons for the change and they provide useful information for stakeholders. Some but not all describe the general source of the change and there is no information on the details of the change itself.
Looking at the options we can pretty quickly eliminate two of them.
b) can be eliminated as there is no information on the table regarding the source of the change.
Likewise c) cannot be right either, as there is not any information on the details of the changes.
a) is correct as there is clear reasons for the changes being made in the Details of change column, as well as dates and a version number, which is useful for an audit trail.
d) is correct as the table does provide information at a useful level for stakeholders, they can see what changes are being made and what version of the system those changes are taking effect from.
Question 19
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A Software development teams must adopt a project structure in order to ensure that software is delivered to time, quality and cost.
B Software development teams using waterfall methods of development should adopt a functional structure reporting to a software development manager.
C Software development teams using agile methods should adopt a matrix structure that allows for complete flexibility of roles across the team.
D Software development teams should adopt a structure that is appropriate for their organisation, irrespective of whether project working is used.
Answer
D Software development teams should adopt a structure that is appropriate for their organisation, irrespective of whether project working is used.
Structures may vary depending mainly on organisational considerations. Structures may also vary depending on the methodology, but the options focusing on method are not correct – B is too prescriptive and C is too flexible.
So I think the answer key explains it better than I do, I don’t know what a project structure, functional structure or matrix structure looks like. However I did go for D when I attempted the paper, to me it made the most sense. It is better to adopt a structure suited to your business, then pick a methodology that is appropriate for that structure. The others are too specific.
Here is an image which hopefully shows the differences between them:
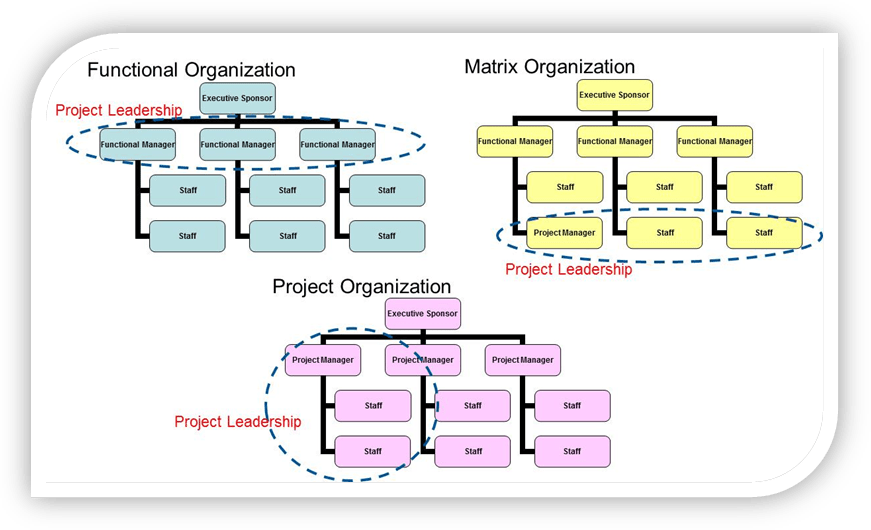
Question 20
A software development project has encountered a problem. The code development is taking longer than planned and has failed to reach a key milestone. The code developers are blaming the designers, saying that the design is too difficult and it is not possible to get the code working in the time allowed for code development. The designers are blaming the project planners, saying that the plan did not take proper account of the likely complexity of the design. The planners have said that the code developers are at fault as they do not have the skills needed to get the code developed in the timescale required.
Where does the responsibility lie for resolving the problem?
A The project planners.
B The software designers.
C The project manager.
D The software code development manager.
Answer
C The project manager.
Because this software development is governed by a project this typical project problem is the responsibility of the project manager to address and resolve. The resolution may of course involve the other parties.
So again the Project Manager has little mentions in the syllabus, but the way I thought about this one was that nobody was happy with the deliverables that were passed down to them, and the Project Manager should be involved in the sign off of the deliverables at every stage in the project. Therefore they would be to blame for the issues, and C is the correct answer. They should be the liaison between the various teams involved and will therefore be the ones who have to resolve issues like this.

After going through your blogs, i was able to pass my BCS methodology exam. Do you have anything for Software developers L4 language exam. Thank you very much.
LikeLike